Projects
Improving reliability for federated learning through model calibration
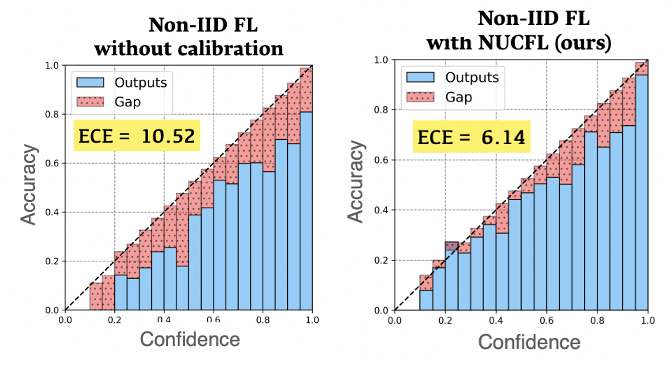
Generating trustworthy predictions is critical for AI/ML, but there is scarce research addressing reliability issues in distributed machine learning. We found that federated learning suffers from more severe miscalibration issues compared to centralized learning. To tackle this challenge, we propose the first model calibration approach for federated learning. Our method considers global calibration needs during local training through a similarity-based approach, improving model calibration while maintaining performance.
[ICLR'25]
Generating trustworthy predictions is critical for AI/ML, but there is scarce research addressing reliability issues in distributed machine learning. We found that federated learning suffers from more severe miscalibration issues compared to centralized learning. To tackle this challenge, we propose the first model calibration approach for federated learning. Our method considers global calibration needs during local training through a similarity-based approach, improving model calibration while maintaining performance.
[ICLR'25]
Fairness-aware pre-training for federated learning
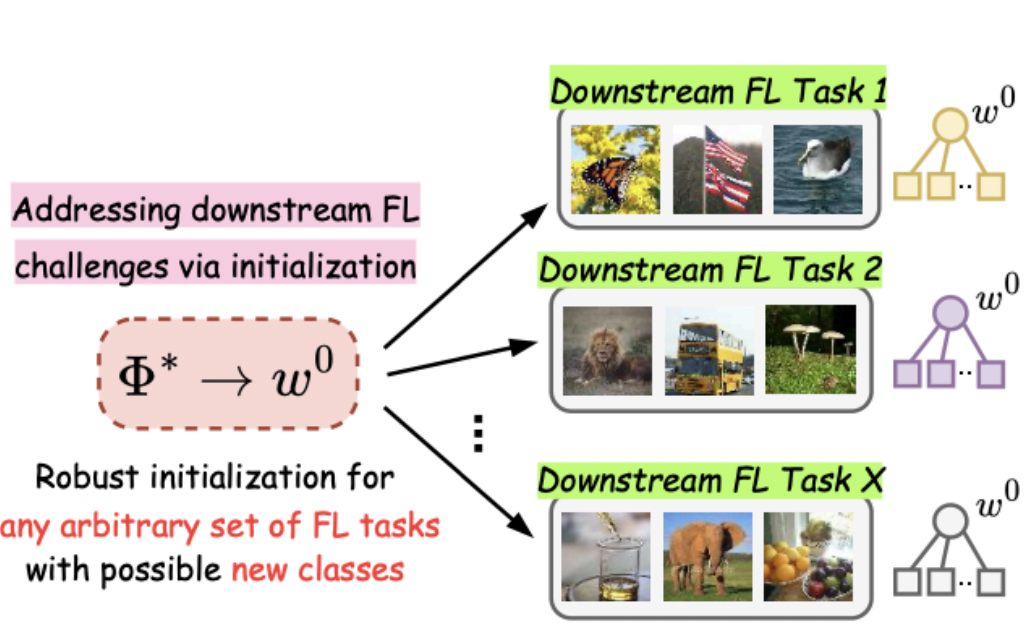
The initialization issue has received relatively little attention in distributed machine learning compared to centralized ML. We found that existing centrally trained pre-trained models introduce performance and fairness concerns for distributed clients. To address this, we propose the first distributed pre-training strategy that provides downstream federated tasks with a robust initialization, inherently improving both performance and fairness.
[AAAI'25]
The initialization issue has received relatively little attention in distributed machine learning compared to centralized ML. We found that existing centrally trained pre-trained models introduce performance and fairness concerns for distributed clients. To address this, we propose the first distributed pre-training strategy that provides downstream federated tasks with a robust initialization, inherently improving both performance and fairness.
[AAAI'25]
Parameter-efficiency for distributed multilingual NLP
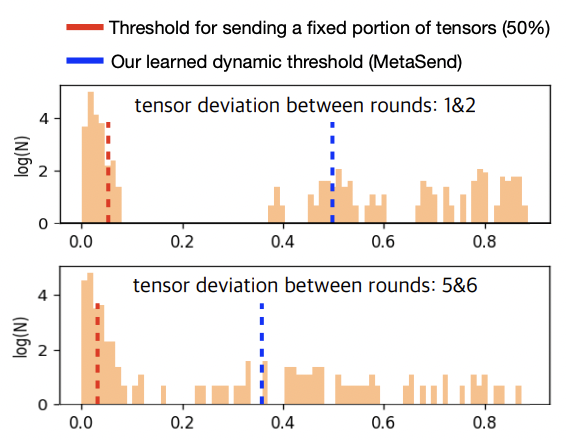
We found that multilingual NLP is a suitable scenario for discussing federated learning since multilingual datasets are often distributed across various locations. However, using large language models introduces a significant communication burden due to the need to exchange a large number of parameters. In this project, we propose a meta-learning-based adaptive parameter selection methodology to improve the communication efficiency of model transmissions from clients in federated multilingual NLP.
[The Web Conf'24 - FL@FM]
We found that multilingual NLP is a suitable scenario for discussing federated learning since multilingual datasets are often distributed across various locations. However, using large language models introduces a significant communication burden due to the need to exchange a large number of parameters. In this project, we propose a meta-learning-based adaptive parameter selection methodology to improve the communication efficiency of model transmissions from clients in federated multilingual NLP.
[The Web Conf'24 - FL@FM]
Improving prediction fairness for minority students in online educational scenarios
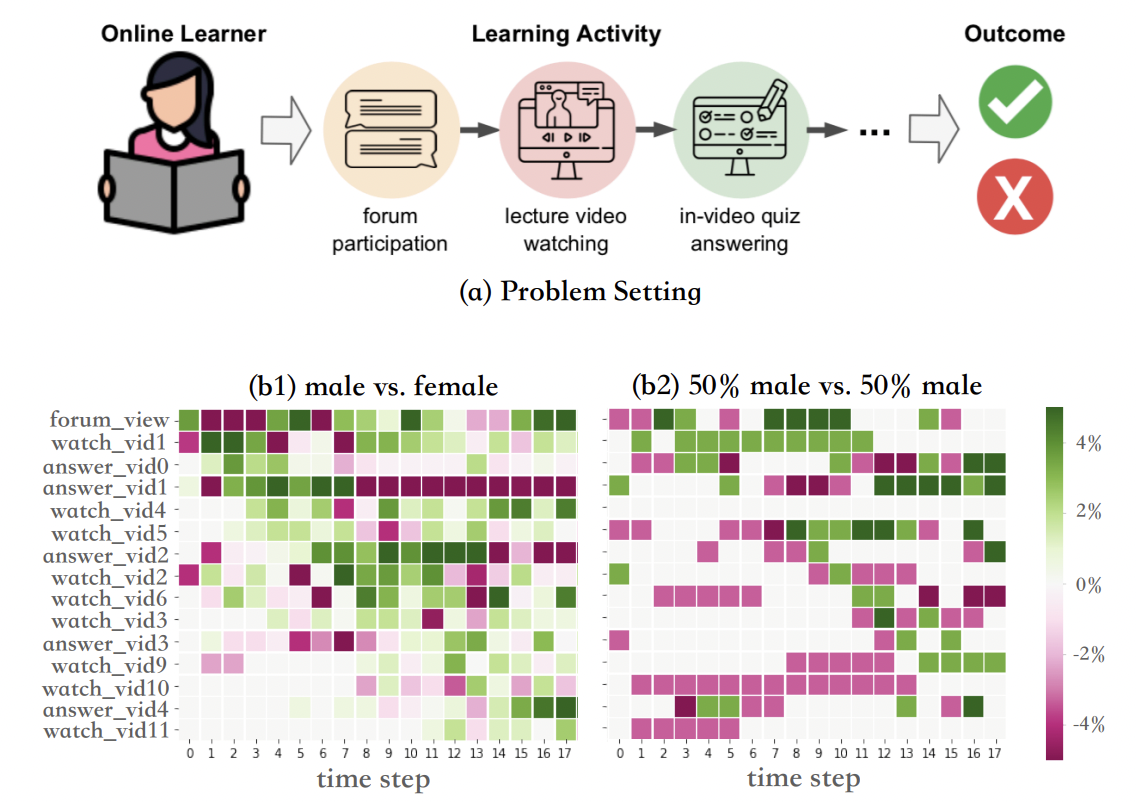
Traditional learning-based approaches to student modeling often generalize poorly to underrepresented student groups due to biases in data availability. We propose a personalized method for predicting student performance based on their online learning activities, optimizing inference accuracy across diverse demographic groups, including race and gender. This project introduces distributed machine learning with meta-learning to customize models for subgroup heterogeneity. Experiments on real-world datasets from online courses demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing student modeling baselines, providing improved predictions of student learning outcomes for all subgroups.
[CIKM '22], [IEEE TETC]
Traditional learning-based approaches to student modeling often generalize poorly to underrepresented student groups due to biases in data availability. We propose a personalized method for predicting student performance based on their online learning activities, optimizing inference accuracy across diverse demographic groups, including race and gender. This project introduces distributed machine learning with meta-learning to customize models for subgroup heterogeneity. Experiments on real-world datasets from online courses demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing student modeling baselines, providing improved predictions of student learning outcomes for all subgroups.
[CIKM '22], [IEEE TETC]

The first reference-free evaluation metric for visual storytelling
It remains unclear whether conventional automatic evaluation metrics for text generation are applicable to Visual Storytelling (VIST). We collect VHED (VIST Human Evaluation Data) dataset, which first re-purposes human evaluation results for automatic evaluation; hence develop VRank (VIST ranker), a novel reference-free VIST metric learned from VHED. Experimental results show that our metric's prediction is significantly more aligned to human evaluation than other metrics with almost 30% higher accuracy when ranking story pairs. Moreover, we demonstrate that only VRank shows human-like behavior in its strong ability to find better stories when the quality gap between two stories is high.
[ACL-IJCNLP'22]
It remains unclear whether conventional automatic evaluation metrics for text generation are applicable to Visual Storytelling (VIST). We collect VHED (VIST Human Evaluation Data) dataset, which first re-purposes human evaluation results for automatic evaluation; hence develop VRank (VIST ranker), a novel reference-free VIST metric learned from VHED. Experimental results show that our metric's prediction is significantly more aligned to human evaluation than other metrics with almost 30% higher accuracy when ranking story pairs. Moreover, we demonstrate that only VRank shows human-like behavior in its strong ability to find better stories when the quality gap between two stories is high.
[ACL-IJCNLP'22]
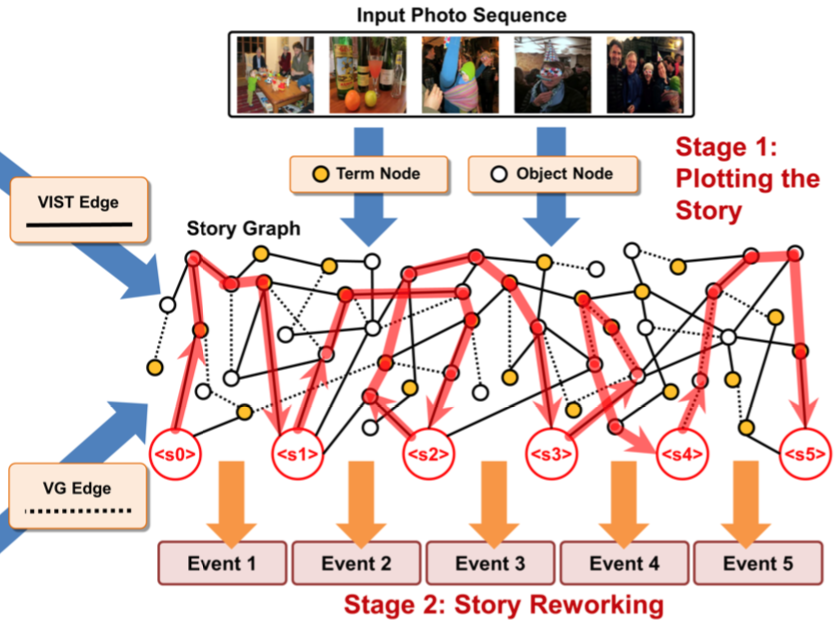
Modeling Storylines for Visual Storytelling
Writing a coherent and engaging story is not easy, especially for automated visual storytelling models. We introduce PR-VIST, a framework that first represents the input image sequence as a story graph in which it finds the best path to form a storyline. PR-VIST then takes this path and learns to generate and refine the final story via Transformer with a human-like discriminator. This framework produces stories that are superior in terms of diversity, coherence, and humanness, per both automatic and human evaluations. An ablation study shows that both plotting and reworking contribute to the model's superiority.
[ACL-IJCNLP'21 Findings]
Writing a coherent and engaging story is not easy, especially for automated visual storytelling models. We introduce PR-VIST, a framework that first represents the input image sequence as a story graph in which it finds the best path to form a storyline. PR-VIST then takes this path and learns to generate and refine the final story via Transformer with a human-like discriminator. This framework produces stories that are superior in terms of diversity, coherence, and humanness, per both automatic and human evaluations. An ablation study shows that both plotting and reworking contribute to the model's superiority.
[ACL-IJCNLP'21 Findings]
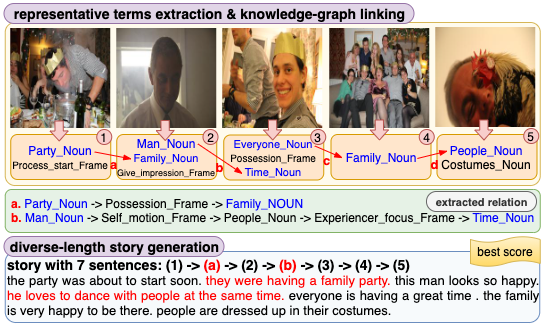
Getting Flexible With Visual Stories
Most visual storytelling models remain limited in terms of the generated stories' fixed length, and the fix-length stories carry limited details and provide ambiguous textual information to the readers. Therefore, we propose Stretch-VST to generate prolonged stories by adding appropriate knowledge. The framework distills representative terms from a sequence of images and find the appropriate relations between terms on knowledge graph by a scoring function. We also design a length-controlled Transformer to generate diverse length stories with better focus and detail compared to the state of the art.
[ACL-IJCNLP'21 Demo]
Most visual storytelling models remain limited in terms of the generated stories' fixed length, and the fix-length stories carry limited details and provide ambiguous textual information to the readers. Therefore, we propose Stretch-VST to generate prolonged stories by adding appropriate knowledge. The framework distills representative terms from a sequence of images and find the appropriate relations between terms on knowledge graph by a scoring function. We also design a length-controlled Transformer to generate diverse length stories with better focus and detail compared to the state of the art.
[ACL-IJCNLP'21 Demo]

Conversational Visual Question Generation
Explored a novel scenario: a conversation agent views a set of the user's photos and asks an engaging question to initiate a conversation with the user. Introduced a two-phase framework that first generates a visual story for the photo set and then uses the story to produce an interesting question. The human evaluation shows that our framework generates more response-provoking questions for starting conversations than other vision-to-question baselines.
[AAAI'21 - DIAL]
Explored a novel scenario: a conversation agent views a set of the user's photos and asks an engaging question to initiate a conversation with the user. Introduced a two-phase framework that first generates a visual story for the photo set and then uses the story to produce an interesting question. The human evaluation shows that our framework generates more response-provoking questions for starting conversations than other vision-to-question baselines.
[AAAI'21 - DIAL]
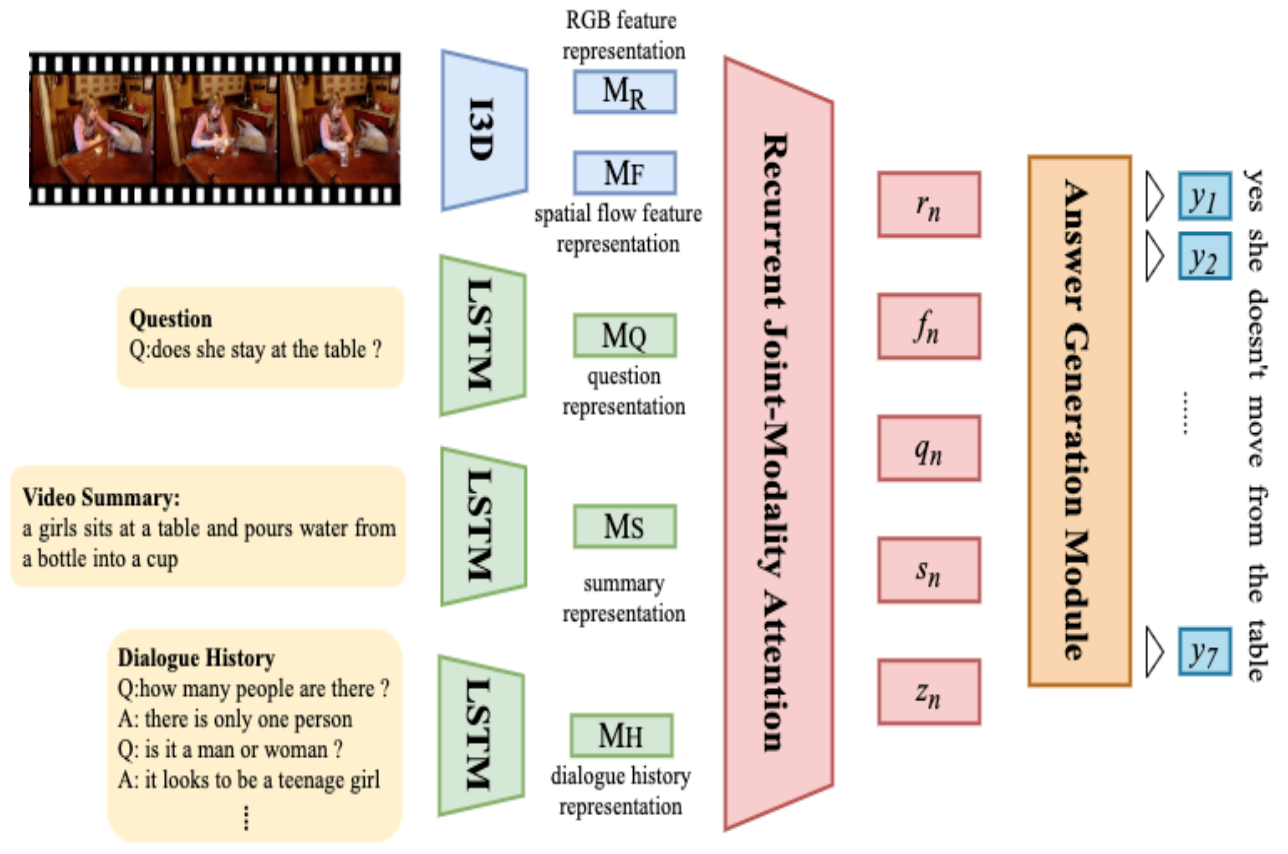
Multi-modal Dialog System
Proposed a multi-step joint-modality attention network based on recurrent neural network to reason on multiple modalities, including audio, vision, and language. The model jointly considered both visual and textual representations in each reasoning process to better integrate information from dynamic scenes.
[IEEE/ACM TASLP], [AAAI'20 - DSTC]
Proposed a multi-step joint-modality attention network based on recurrent neural network to reason on multiple modalities, including audio, vision, and language. The model jointly considered both visual and textual representations in each reasoning process to better integrate information from dynamic scenes.
[IEEE/ACM TASLP], [AAAI'20 - DSTC]
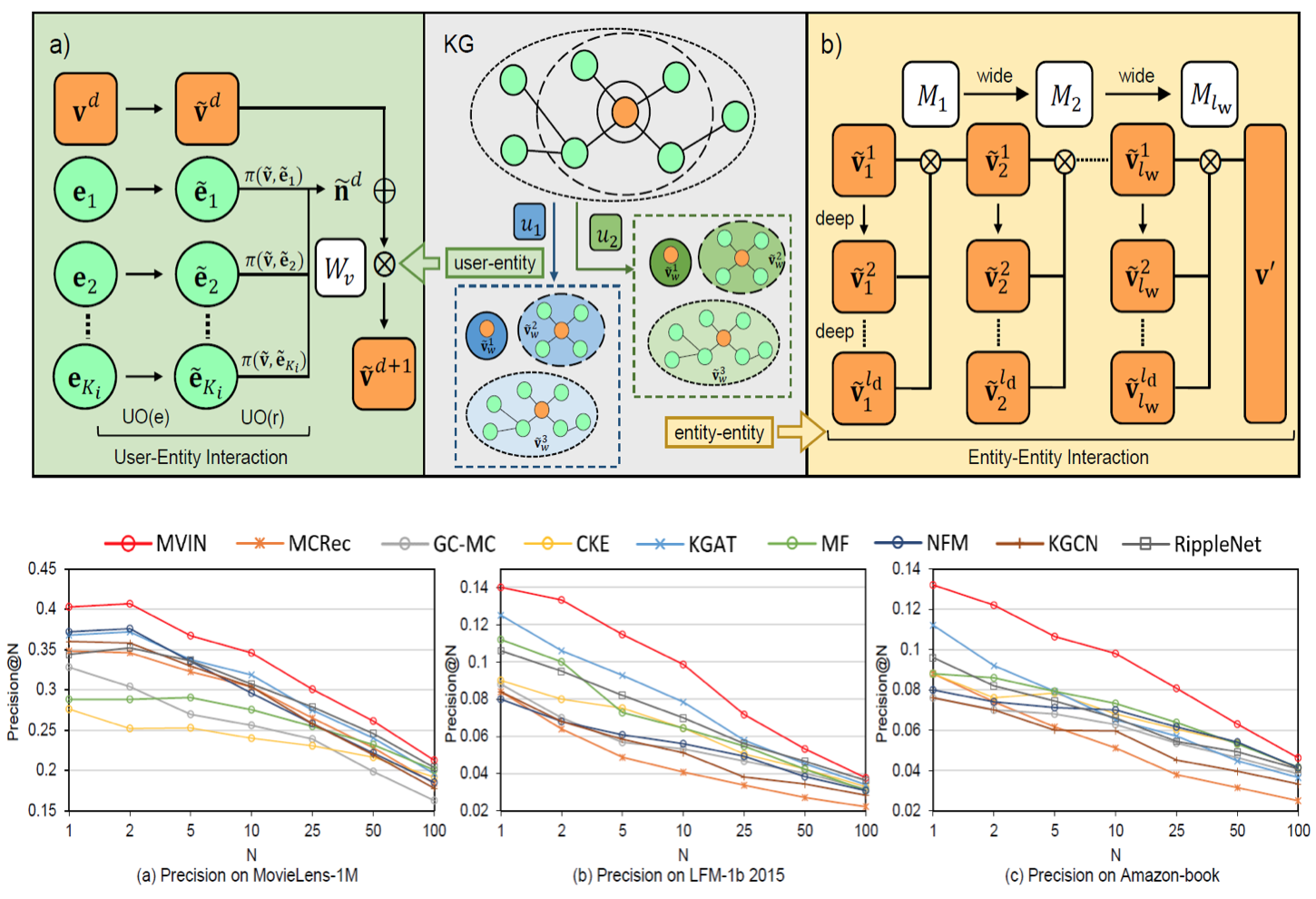
Multiview Items Recommendation
Developed a GNN-based recommendation model which provides superior recommendations by describing items from user and entity angles. Designed user-oriented modules that aggregate features to make personalized recommendations and a mixing layer which contrasts layer-wise GCN to obtain comprehensive features from internal entity-entity interactions.
[SIGIR'20]
Developed a GNN-based recommendation model which provides superior recommendations by describing items from user and entity angles. Designed user-oriented modules that aggregate features to make personalized recommendations and a mixing layer which contrasts layer-wise GCN to obtain comprehensive features from internal entity-entity interactions.
[SIGIR'20]
